Easy, Advanced and Fast Internationalization for your Flutter Apps
About this library
- ✅ Fully tested code (100% code coverage)
- 🌐 Easy translations for many languages
- 🛡️ Null safety
- 📂 Load translations from JSON file
- 🧩 Extension methods on BuildContext, String and Text
- 🚀 Supports plural, nesting, choice, RTL locales and more
- ↩️ Fallback locale keys redirection (Optional)
- 💾 Persistent locale storage (Optional)
- ❗ Error widget for missing translations
- 🎧 Listening to localization changes via controller
- 🔁 Context independent locale change via controller
Installation
Add to your pubspec.yaml:
dependencies: localization_plus: <last_version>
Create folder and add translation files like this
i18n
├── {languageCode}.{ext} // useOnlyLangCode: true
└── {languageCode}-{countryCode}.{ext} // useOnlyLangCode: false (default)
Example:
i18n
├── en.json
└── en-US.json
Declare your assets localization directory in pubspec.yaml:
flutter:
assets:
- i18n/
🚨 Note on iOS
For translation to work on iOS you need to add supported locales to ios/Runner/Info.plist as described here.
Example:
<key>CFBundleLocalizations</key> <array> <string>en</string> <string>nb</string> </array>
Documentation
📄 LocalizationPlusController properties
PropertiesRequiredDefaultDescriptionsupportedLocalestrueList of supported locales.pathtruePath to your folder with localization files.loaderfalseRootBundleAssetLoader()Class loader for localization files. You can create your own class.saveLocalefalsetrueWhether to save on the device after changing the languageuseOnlyLangCodefalsefalseTrigger for using only language code for reading localization files.Example:en.json //useOnlyLangCode: trueen-US.json //useOnlyLangCode: false (default)useFallbackTranslationsfalsefalseIf a localization key is not found in the locale file, try to use the fallbackLocale file. sets the first supported language as fallback if fallback locale is not setfallbackLocalefalseSet the locale to be used as an alternative if a localization key is not found in the locale filestartLocalefalseIf there is no saved language, set the language in which the system will start
📄 LocalizationPlus widget properties
PropertiesRequiredDefaultDescriptionkeyfalseWidget key.childtruePlace for your main page widget.controllertrueLocalizationPlusController instance .
Replacing Parameters In Translation Strings
If you wish, you may define placeholders in your translation strings. All placeholders must be between curly brackets. For example, you may define a welcome message with a placeholder name:
{
"welcome": "Welcome, {name}"
}
If your placeholder contains all capital letters, or only has its first letter capitalized, the translated value will be capitalized accordingly:
"welcome": "Welcome, {NAME}" // Welcome, USER
"welcome": "Welcome, {Name}" // Welcome, User
Usage/Examples
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:localization_plus/localization_plus.dart';
void main() async {
WidgetsFlutterBinding.ensureInitialized();
// If you wish, you can define it so that it can be accessed
// from anywhere in the system with a package such as the getIt library
LocalizationPlusController controller = await LocalizationPlusController.init(
path: 'i18n',
);
runApp(
LocalizationPlus(
controller: controller,
supportedLocales: [
'en_US'.toLocale(),
'ar_DZ'.toLocale(),
'tr_TR'.toLocale(),
'ru_RU'.toLocale(),
],
child: const MyApp()
),
);
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
// Localizations
localizationsDelegates: context.localizationDelegates,
supportedLocales: context.supportedLocales,
locale: context.locale,
home: MyHomePage()
);
}
}
🔥 Change locale
You can change the locale with the help of BuildContext extension method or controller.
// via context
context.setLocale('en_US'.toLocale());
// via controller
controller.setLocale('en_US'.toLocale());
🔥 Reset locale resetLocale()
Reset locale to initial locale. Sets startLocale to startLocale if startLocale is defined, to deviceLocale if not defined
// via context context.resetLocale() // via controller controller.resetLocale();
🔥 Delete saved locale deleteSavedLocale()
Clears a saved locale from local storage
// via context context.deleteSavedLocale() // via controller controller.deleteSavedLocale();
🔥 Get locale currentLocale
Returns the current locale in the application
// via context context.currentLocale; // via controller controller.currentLocale;
🔥 Get device locale deviceLocale
Returns the device locale
// via context context.deviceLocale // via controller controller.deviceLocale
🔥 Get fallback locale fallbackLocale
Returns the fallback locale. Returns null if useFallbackTranslations is false
// via context context.fallbackLocale // via controller controller.fallbackLocale
🔥 Translate trans()
Main function for translate your language keys
You can use extension methods of [String] or [Text] widget, you can also use trans() as a helper function.
Example:
{
"notations": "Default: {arg}, Capital: {Arg}, Uppercase: {ARG}",
}
'notations'.trans(arguments: {'arg': 'test'}) // String
// Result: Default: test, Capital: Test, Uppercase: TEST
const Text('notations').trans(arguments: {'arg': 'test'}) // Text
// Result: Text instance
trans('notations', arguments: {'arg': 'test'}) // Helper function
// Result: Default: test, Capital: Test, Uppercase: TEST
Arguments:
NameTypeDescriptionargumentsMap<String, String>Map of localized strings. Replaces the name keys {key_name} according to its name
🔥 Plurals plural()
Pluralization is a complex problem, as different languages have a variety of complex rules for pluralization; however, Localization Plus can help you translate strings differently based on pluralization rules that you define.
You can use extension methods of [String] or [Text] widget, you can also use plural() as a helper function.
🚨 Key “other” required!
Example:
{
"clicked": {
"zero": "Today",
"one": "Tomorrow",
"two": "2 days later",
"few": "A few days later",
"many": "Weeks later",
"other": "After a long time"
}
}
// String
'clicked'.plural(0) // Today
'clicked'.plural(1) // Tomorrow
'clicked'.plural(2) // 2 days late
'clicked'.plural(3) // A few days later (Depends on the language)
'clicked'.plural(11) // Weeks later (Depends on the language)
'clicked'.plural(1250) // After a long time (Depends on the language)
// Text
Text('clicked').plural(0) // Today
Text('clicked').plural(1) // Tomorrow
Text('clicked').plural(2) // 2 days late
Text('clicked').plural(3) // A few days later (Depends on the language)
Text('clicked').plural(11) // Weeks later (Depends on the language)
Text('clicked').plural(1250) // After a long time (Depends on the language)
plural('clicked', 0) // Today
plural('clicked', 1) // Tomorrow
plural('clicked', 2) // 2 days late
plural('clicked', 3) // A few days later (Depends on the language)
plural('clicked', 11) // Weeks later (Depends on the language)
plural('clicked', 1250) // After a long time (Depends on the language)
Arguments:
NameTypeDescriptionargumentsMap<String, String>Map of localized strings. Replaces the name keys {key_name} according to its name
🔥 Trans Choice transChoice()
You may create more complex pluralization rules which specify translation strings for multiple ranges of values.
You can use extension methods of [String] or [Text] widget, you can also use transChoice() as a helper function.
Example:
{
"price": {
"0": "Free",
"1:5": "Cheap",
"6:10": "Normal",
"*": "Expensive"
}
}
// String
'price'.transChoice(0) // Free
'price'.transChoice(1) // Cheap
'price'.transChoice(3) // Cheap
'price'.transChoice(6) // Normal
'price'.transChoice(10) // Normal
'price'.transChoice(1250) // Expensive
// Text
('price').transChoice(0) // Free
('price').transChoice(1) // Cheap
('price').transChoice(3) // Cheap
('price').transChoice(6) // Normal
('price').transChoice(10) // Normal
('price').transChoice(1250) // Expensive
transChoice('price', 0) // Free
transChoice('price', 1) // Cheap
transChoice('price', 3) // Cheap
transChoice('price', 6) // Normal
transChoice('price', 10) // Normal
transChoice('price', 1250) // Expensive
Arguments:
NameTypeDescriptionargumentsMap<String, String>Map of localized strings. Replaces the name keys {key_name} according to its name
🔥 Listening for locale change
You can listen to locale changes with the help of the controller.
controller.addListener(() {
// Locale changed
// Refetch language dependent remote data etc.
});
🔥 Linked translations:
If there’s a translation key that will always have the same concrete text as another one you can just link to it. To link to another translation key, all you have to do is to prefix its contents with an @: sign followed by the full name of the translation key including the namespace you want to link to.
{
"hello": "Hello",
"world": "World",
"hello_world": "@:hello @:world"
}
You can also do nested anonymous and named arguments inside the linked messages.
Formatting linked translations:
If the language distinguishes cases of character, you may need to control the case of the linked locale messages. Linked messages can be formatted with modifier @.modifier:key
The below modifiers are available currently.
upper: Uppercase all characters in the linked message.lower: Lowercase all characters in the linked message.capitalize: Capitalize the first character in the linked message.
xample:
{
...
"hello": "Hello",
"world": "World",
"hello_world": "@.upper:hello @.lower:world" // HELLO world
...
}
🔥 Check translation exists transExists()
You can check if a key has a translation
'notations'.transExists() // String
// Result: true
transExists('not_exists') // Helper function
// Result: false
🧩 Extensions
String Extension
'en_US'.toLocale(); // Locale('en', 'US')
//with custom separator
'en|US'.toLocale(separator: '|') // Locale('en', 'US')
Build Context Extension
context.currentLocale // get current locale context.deviceLocale // get device locale context.fallbackLocale // get fallback locale context.supportedLocales // get supported locales context.localizationDelegates // get localization delegates
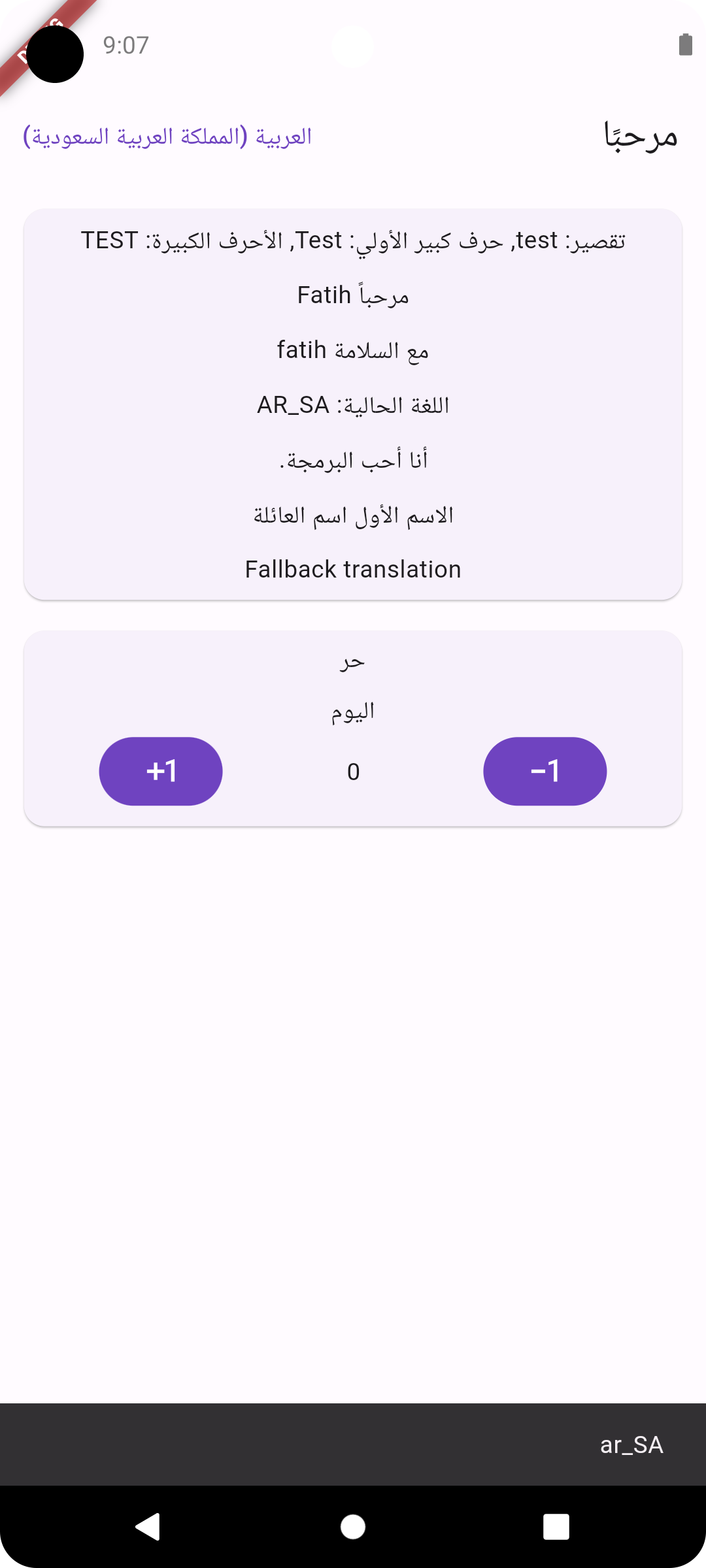
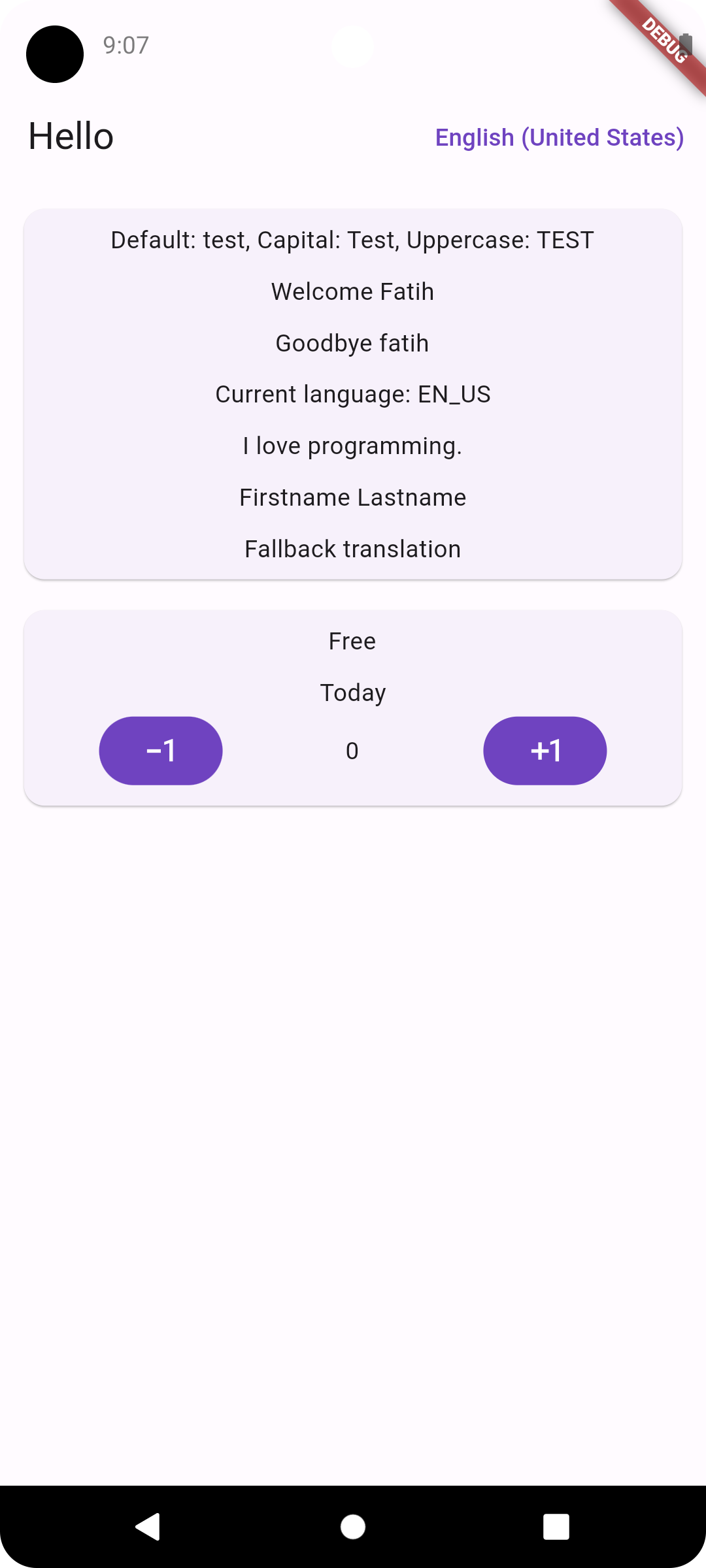
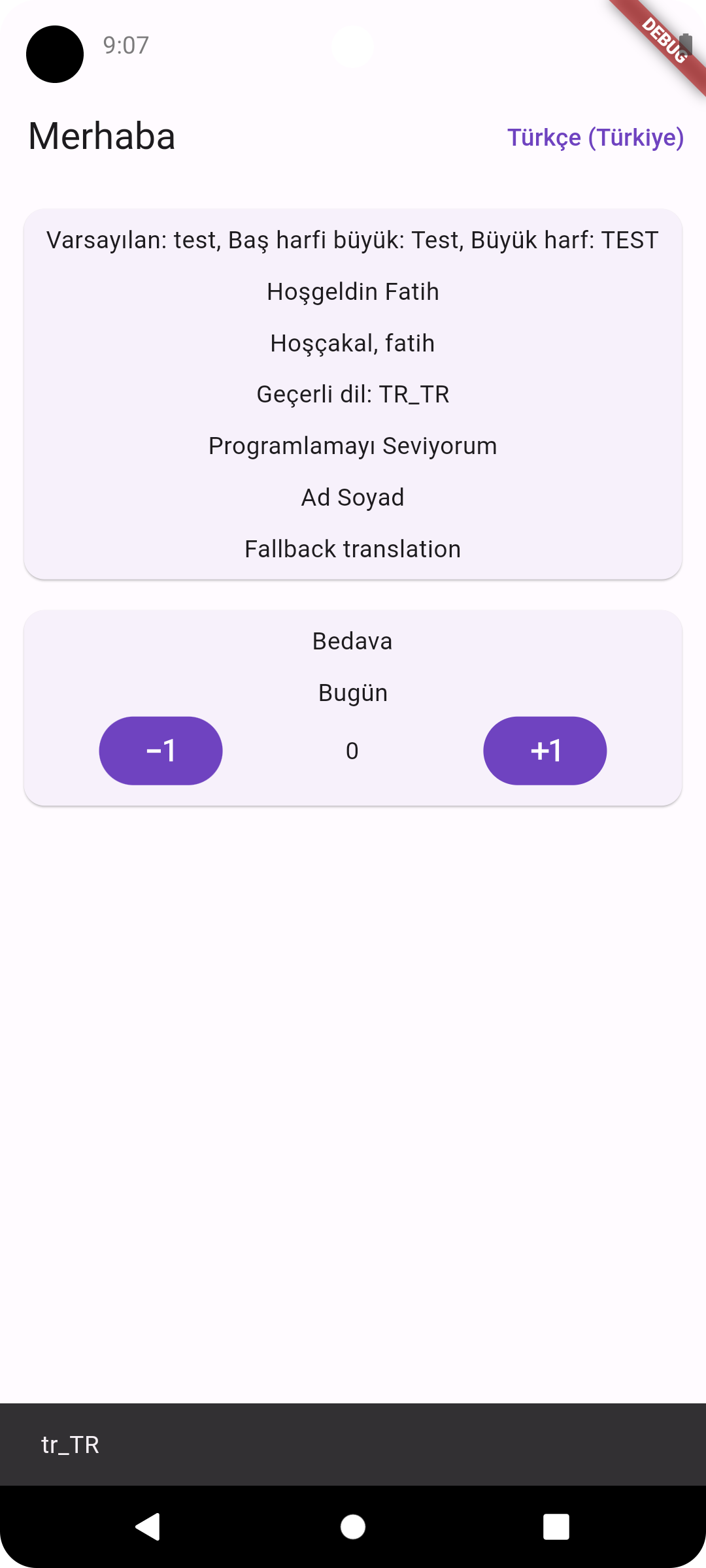
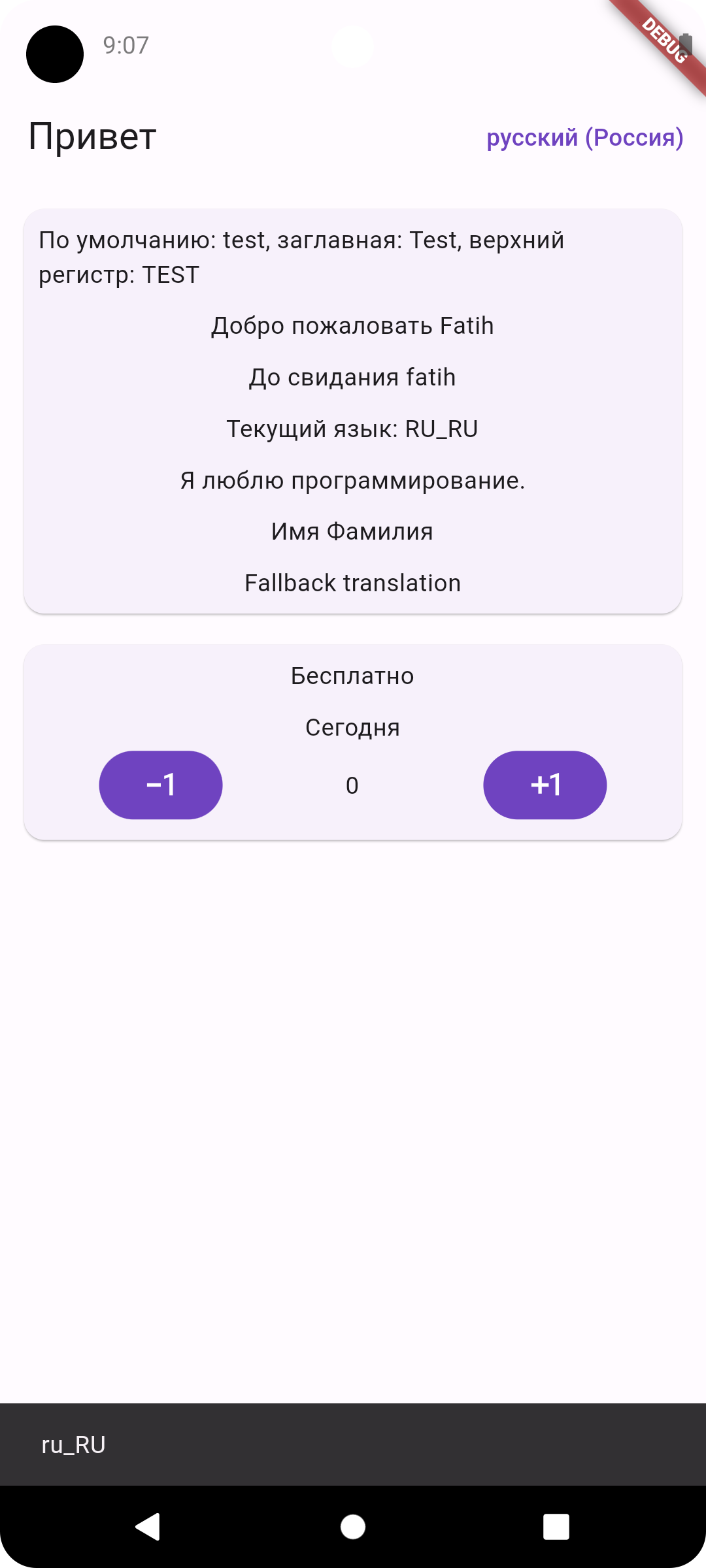
Screenshots
Arabic RTLEnglish LTRTurkish LTRRussian LTR